I have the DS220J. Ive found a couple instructions online on how to setup an Open VPN on the NAS for the Private Internet Access VPN which I have. After following them Im cannot get the VPN to work. I chatted with PIA support that they said they dont support NAS which is odd since on their site they also have instructions to install it. There's little contest between ExpressVPN, one of the top 3 services of its kind currently on the market, and HideMyAss, a VPN that might be decent for Pia Vpn On Synology light applications, but is certainly not secure enough for more sensitive data.
Set up VPN Server
With the VPN Server package, you can easily turn your Synology NAS into a VPN server to allow DSM users to remotely and securely access resources shared within the local area network of your Synology NAS. By integrating common VPN protocols - PPTP, OpenVPN and L2TP/IPSec - VPN Server provides options to establish and manage VPN services tailored to your individual needs. To choose any of the following types of VPN server and to enable VPN services on your Synology NAS, install and launch VPN Server. Hermes postage prices.
Note:
- Enabling VPN service affects the network performance of the system.
- Only DSM users belonging to the administrators group can install and set up VPN Server.
PPTP
PPTP (Point-to-Point Tunneling Protocol) is a commonly used VPN solution supported by most clients (including Windows, Mac, Linux, and mobile devices). For more information about PPTP, refer to here.
To enable PPTP VPN server:
- Open VPN Server and then go to Settings > PPTP on the left panel.
- Tick Enable PPTP VPN server.
- Specify a virtual IP address of VPN server in the Dynamic IP address fields. Refer to About Dynamic IP Address below for more information.
- Set Maximum connection number to limit the number of concurrent VPN connections.
- Set Maximum number of connections with same account to limit the number of concurrent VPN connections with the same account.
- Choose either of the following from the Authentication drop-down menu to authenticate VPN clients:
- PAP: VPN clients' passwords will not be encrypted during authentication.
- MS-CHAP v2: VPN clients' passwords will be encrypted during authentication using Microsoft CHAP version 2.
- If you selected MS-CHAP v2 for authentication above, choose any of the following from the Encryption drop-down menu to encrypt VPN connection:
- No MPPE: VPN connection will not be protected with Microsoft Point-to-Point Encryption(MPPE) mechanism.
- Optional MPPE: If the client enables MPPE mechanism, VPN connection will be protected with MPPE mechanism. Otherwise, VPN connection will not be protected.
- Require MPPE: VPN connection will be protected with MPPE mechanism.
- Set MTU (Maximum Transmission Unit) to limit data packet size transmitted via the VPN.
- Tick Use manual DNS and specify the IP address of a DNS server to push DNS to PPTP clients. If this option is disabled, the DNS server used by the Synology NAS will be pushed to clients.
- Click Apply for the changes to take effect.
Note:
- When connecting to the VPN, the authentication and encryption settings of VPN clients must be identical to the settings specified on VPN Server, or else clients will not be able to connect successfully.
- To be compatible with most PPTP clients running Windows, Mac OS, iOS and Android operating systems, the default MTU is set to 1400. For more complicated network environments, a smaller MTU might be required. Try to reduce the MTU size if you keep receiving timeout error or experience unstable connections.
- Please check the port forwarding and firewall settings on your Synology NAS and router to make sure the TCP port 1723 is open.
- PPTP VPN service is built-in on some routers, the port 1723 might be occupied. To ensure VPN Server works properly, you might need to disable the built-in PPTP VPN service through the router's management interface to have the PPTP of VPN Server work. In addition, some old routers block the GRE protocol (IP protocol 47), which will result in VPN connection failure. It is recommended using a router that supports VPN pass-through connections.
OpenVPN
OpenVPN is an open source solution for implementing VPN service. It protects the VPN connection with the SSL/TLS encryption mechanism. For more information about OpenVPN, visit here.
To enable OpenVPN VPN server:
- Open VPN Server and then go to Settings > OpenVPN on the left panel.
- Tick Enable OpenVPN server.
- Specify a virtual internal IP address of VPN server in the Dynamic IP address fields. Refer to About Dynamic IP Address below for more information.
- Set Maximum connection number to limit the number of concurrent VPN connections.
- Set Maximum number of connections with same account to limit the number of concurrent VPN connections with the same account.
- Tick Enable compression on the VPN link if you want to compress data during transfer. This option can increase transmission speed, but might consume more system resources.
- Tick Allow clients to access server's LAN to permit clients to access the server's LAN.
- Tick Enable IPv6 server mode to enable OpenVPN server to send IPv6 addresses. You will first need to get a prefix via 6in4/6to4/DHCP-PD in Control Panel > Network > Network Interface. Then select the prefix in this page.
- Click Apply for the changes to take effect.
Note:
- VPN Server does not support bridge mode for site-to-site connections.
- Please check the port forwarding and firewall settings on your Synology NAS and router to make sure the UDP port 1194 is open.
- When running OpenVPN GUI on Windows Vista or Windows 7, please note that UAC (User Account Control) is enabled by default. If enabled, you need to use the Run as administrator option to properly connect with OpenVPN GUI.
- When enabling IPv6 server mode in Windows with OpenVPN GUI, please note the following:
- The interface name used by the VPN cannot have a space, e.g., LAN 1 needs to be changed to LAN1.
- The option redirect-gateway has to be set in the openvpn.ovpn file at the client side. If you do not want to set this option, you should set the DNS of the VPN interface manually. You may use Google IPv6 DNS: 2001:4860:4860::8888.
- When Allow clients to access server's LAN is not ticked, VPN clients will still be able to access your server's LAN in the following situations:
- VPN server is set as the default gateway at the client side.
- Related routing rules are added manually at the client side.
To export configuration file:
Click Export Configuration. OpenVPN allows VPN server to issue an authentication certificate to the clients. The exported file is a zip file that contains ca.crt (certificate file for VPN server), openvpn.ovpn (configuration file for the client), and README.txt (simple instruction on how to set up OpenVPN connection for the client). For more information, refer to here.
Note:
- Each time VPN Server runs, it will automatically copy and use the certificate shown at Control Panel > Security > Certificate. If you need to use a third-party certificate, please import the certificate at Control Panel > Security > Certificate > Action and restart VPN Server.
- VPN Server will automatically restart each time the certificate file shown at Control Panel > Security > Certificate is modified.
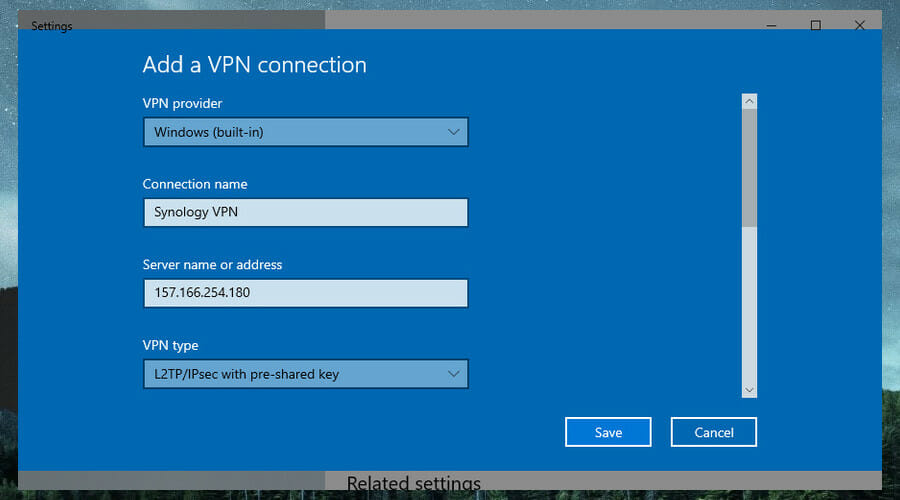
L2TP/IPSec
L2TP (Layer 2 Tunneling Protocol) over IPSec provides virtual private networks with increased security and is supported by most clients (such as Windows, Mac, Linux, and mobile devices). For more information about L2TP, refer to here.
Note:
- To use L2TP/IPSec, make sure your Synology NAS is running DSM 4.3 or later.
To enable L2TP/IPSec VPN server:
- Open VPN Server and then go to Settings > L2TP/IPSec on the left panel.
- Tick Enable L2TP/IPSec VPN server.
- Specify a virtual IP address of VPN server in the Dynamic IP address fields. Refer to About Dynamic IP Address below for more information.
- Set Maximum connection number to limit the number of concurrent VPN connections.
- Set Maximum number of connections with same account to limit the number of concurrent VPN connections with the same account.
- Choose either of the following from the Authentication drop-down menu to authenticate VPN clients:
- PAP: VPN clients' passwords will not be encrypted during authentication.
- MS-CHAP v2: VPN clients' passwords will be encrypted during authentication using Microsoft CHAP version 2.
- Set MTU (Maximum Transmission Unit) to limit data packet size transmitted via the VPN.
- Tick Use manual DNS and specify the IP address of a DNS server to push DNS to L2TP/IPSec clients. If this option is disabled, the DNS server used by the Synology NAS will be pushed to clients.
- Enter and confirm a pre-shared key. This secret key should be given to your L2TP/IPSec VPN user to authenticate the connection.
- Click Apply for the changes to take effect.
Note:
- When connecting to the VPN, the authentication and encryption settings of VPN clients must be identical to the settings specified on VPN Server, or else clients will not be able to connect successfully.
- To be compatible with most L2TP/IPSec clients running Windows, Mac OS, iOS, and Android operating systems, the default MTU is set to 1400. For more complicated network environments, a smaller MTU might be required. Try to reduce the MTU size if you keep receiving timeout error or experience unstable connection.
- Please check the port forwarding and firewall settings on your Synology NAS and router to make sure the UDP port 1701, 500, and 4500 are open.
- L2TP or IPSec VPN service is built-in on some routers, the port 1701, 500 or 4500 might be occupied. To ensure VPN Server works properly, you might need to disable the built-in L2TP or IPSec VPN service through the router's management interface to have the L2TP/IPSec of VPN Server work. It is recommended using a router that supports VPN pass-through connections.
About Dynamic IP Address
Depending on the number you entered in Dynamic IP address, VPN Server will choose from a range of virtual IP addresses while assigning IP addresses to VPN clients. For example, if the dynamic IP address of VPN server is set as '10.0.0.0', a VPN client's virtual IP address could range from '10.0.0.1' to '10.0.0.[maximum connection number]' for PPTP, and from '10.0.0.2' to '10.0.0.255' for OpenVPN.
Important:Before specifying the dynamic IP address of VPN server, please note:
- Dynamic IP addresses allowed for VPN server should be any of the following:
- From '10.0.0.0' to '10.255.255.0'
- From '172.16.0.0' to '172.31.255.0'
- From '192.168.0.0' to '192.168.255.0'
- The specified dynamic IP address of VPN server and the assigned virtual IP addresses for VPN clients should not conflict with any IP addresses currently used within your local area network.
About Client's Gateway Setting for VPN Connection
Before connecting to the local area network of Synology NAS via VPN, the clients might need to change their gateway setting for VPN connection. Otherwise, they might not be able to connect to the Internet when VPN connection is established. For detailed information, refer to here.
A few years ago, a close friend of mine was hit with a subpoena claiming that his unsecured WiFi network was used to illegally pirate movies. Though they may have never been able to prove who exactly was pirating the movies, the legal fees would have cost thousands just to prove their innocence.
Ever since then, I've been an advocate for using VPNs to protect your privacy when browsing the web.
When I upgraded my storage solution to a NAS, one of the first settings I changed was to route my NAS internet through a VPN.
Unfortunately, this meant all my local browsing was also going through the VPN making everything slow to a crawl.
After many hours of studying different forums, Reddit, and YouTube later, I think I have found the best solution to keep your only your torrent traffic running through a VPN while all other network activities are kept local.
If you enjoy this guide and would like to support additional content creation, consider making a qualifying purchase using any of the affiliate links below.
Private Internet Access Synology Vpn
What you'll need
Here is the setup I used to get this project up and running.
I've been using Private Internet Access for many years and they work perfectly with this guide. You can check the latest pricing information here.
If you decide to use a different VPN, this guide should still get you at least 95% of the way there. Check out their respective communities on Reddit or reach out to your VPN's customer support for any additional steps.
- NAS: Synology DS918+
- DSM Version: 6.2.2 and newer
- VPN: Private Internet Access
Installation Steps
Install Docker
1. Find and install Docker in the Package Center.
2. Search the registry for haugene
3. Download the latest image for haugene/transmission-openvpn
While the image is downloading, we'll complete the next steps.
Create Transmission Directory
Next, we'll create a couple of folders. One for your Transmission configuration files and another for your downloads.
- Inside the docker folder, create a folder named transmission-openvpn
- In your root directory, create a folder named Downloads
Create Adapter and Configuration File
To create your own files, copy the scripts below into a plain text editor save the files as the following:
Optional: Since these are Google's Public domain nameservers (DNS), this may result in your container leaking website requests. To fix this, change the nameservers to your VPN's public DNS servers.
For PIA users your resolv.confshould look like this:
Free wifi booster virgin. Move these files over to your transmission-openvpn folder.
Schedule Adapter to Run on Boot
1. Open Control Panel
2. Open Task Scheduler
3. Create a Task to run the TUN.sh script on boot-up.
4. In the Task Settings, point to the location of the script.
5. Run the script for the first time.
Launch the Docker Image
Back in Docker, the image should be done downloading now. Launch the image with the following settings:
1. Execute container using high privilege
2. Select Advanced Settings
3. Enable auto-restart
4. Add the resolv.conf file and the Downloads folder.
5. Point the File/Folder to the following mount paths.
5.5 Change the Local Ports from Auto to some unused port numbers.
If you leave this on auto, you will have to constantly look up what port your container has changed to.
6. Add your VPN details into the OpenVPN Environment variables:
| OPENVPN_USERNAME | p00***** |
| OPENVPN_PASSWORD | **password** |
| OPENVPN_PROVIDER | PIA |
You can experiment with the remaining default variables after you have the container up and running.
PIA NextGen Updates
PIA has updated their VPN network to NextGen which has broken previous containers.
If you're having trouble launching your old containers, delete all of your old images and containers.
Redownload the latest image and add the additional environmental variables:
Pia Vpn On Synology Download
| OPENVPN_CONFIG | ca_montreal |
| PIA_OPENVPN_CONFIG_BUNDLE | openvpn |

PPTP (Point-to-Point Tunneling Protocol) is a commonly used VPN solution supported by most clients (including Windows, Mac, Linux, and mobile devices). For more information about PPTP, refer to here.
To enable PPTP VPN server:
- Open VPN Server and then go to Settings > PPTP on the left panel.
- Tick Enable PPTP VPN server.
- Specify a virtual IP address of VPN server in the Dynamic IP address fields. Refer to About Dynamic IP Address below for more information.
- Set Maximum connection number to limit the number of concurrent VPN connections.
- Set Maximum number of connections with same account to limit the number of concurrent VPN connections with the same account.
- Choose either of the following from the Authentication drop-down menu to authenticate VPN clients:
- PAP: VPN clients' passwords will not be encrypted during authentication.
- MS-CHAP v2: VPN clients' passwords will be encrypted during authentication using Microsoft CHAP version 2.
- If you selected MS-CHAP v2 for authentication above, choose any of the following from the Encryption drop-down menu to encrypt VPN connection:
- No MPPE: VPN connection will not be protected with Microsoft Point-to-Point Encryption(MPPE) mechanism.
- Optional MPPE: If the client enables MPPE mechanism, VPN connection will be protected with MPPE mechanism. Otherwise, VPN connection will not be protected.
- Require MPPE: VPN connection will be protected with MPPE mechanism.
- Set MTU (Maximum Transmission Unit) to limit data packet size transmitted via the VPN.
- Tick Use manual DNS and specify the IP address of a DNS server to push DNS to PPTP clients. If this option is disabled, the DNS server used by the Synology NAS will be pushed to clients.
- Click Apply for the changes to take effect.
Note:
- When connecting to the VPN, the authentication and encryption settings of VPN clients must be identical to the settings specified on VPN Server, or else clients will not be able to connect successfully.
- To be compatible with most PPTP clients running Windows, Mac OS, iOS and Android operating systems, the default MTU is set to 1400. For more complicated network environments, a smaller MTU might be required. Try to reduce the MTU size if you keep receiving timeout error or experience unstable connections.
- Please check the port forwarding and firewall settings on your Synology NAS and router to make sure the TCP port 1723 is open.
- PPTP VPN service is built-in on some routers, the port 1723 might be occupied. To ensure VPN Server works properly, you might need to disable the built-in PPTP VPN service through the router's management interface to have the PPTP of VPN Server work. In addition, some old routers block the GRE protocol (IP protocol 47), which will result in VPN connection failure. It is recommended using a router that supports VPN pass-through connections.
OpenVPN
OpenVPN is an open source solution for implementing VPN service. It protects the VPN connection with the SSL/TLS encryption mechanism. For more information about OpenVPN, visit here.
To enable OpenVPN VPN server:
- Open VPN Server and then go to Settings > OpenVPN on the left panel.
- Tick Enable OpenVPN server.
- Specify a virtual internal IP address of VPN server in the Dynamic IP address fields. Refer to About Dynamic IP Address below for more information.
- Set Maximum connection number to limit the number of concurrent VPN connections.
- Set Maximum number of connections with same account to limit the number of concurrent VPN connections with the same account.
- Tick Enable compression on the VPN link if you want to compress data during transfer. This option can increase transmission speed, but might consume more system resources.
- Tick Allow clients to access server's LAN to permit clients to access the server's LAN.
- Tick Enable IPv6 server mode to enable OpenVPN server to send IPv6 addresses. You will first need to get a prefix via 6in4/6to4/DHCP-PD in Control Panel > Network > Network Interface. Then select the prefix in this page.
- Click Apply for the changes to take effect.
Note:
- VPN Server does not support bridge mode for site-to-site connections.
- Please check the port forwarding and firewall settings on your Synology NAS and router to make sure the UDP port 1194 is open.
- When running OpenVPN GUI on Windows Vista or Windows 7, please note that UAC (User Account Control) is enabled by default. If enabled, you need to use the Run as administrator option to properly connect with OpenVPN GUI.
- When enabling IPv6 server mode in Windows with OpenVPN GUI, please note the following:
- The interface name used by the VPN cannot have a space, e.g., LAN 1 needs to be changed to LAN1.
- The option redirect-gateway has to be set in the openvpn.ovpn file at the client side. If you do not want to set this option, you should set the DNS of the VPN interface manually. You may use Google IPv6 DNS: 2001:4860:4860::8888.
- When Allow clients to access server's LAN is not ticked, VPN clients will still be able to access your server's LAN in the following situations:
- VPN server is set as the default gateway at the client side.
- Related routing rules are added manually at the client side.
To export configuration file:
Click Export Configuration. OpenVPN allows VPN server to issue an authentication certificate to the clients. The exported file is a zip file that contains ca.crt (certificate file for VPN server), openvpn.ovpn (configuration file for the client), and README.txt (simple instruction on how to set up OpenVPN connection for the client). For more information, refer to here.
Note:
- Each time VPN Server runs, it will automatically copy and use the certificate shown at Control Panel > Security > Certificate. If you need to use a third-party certificate, please import the certificate at Control Panel > Security > Certificate > Action and restart VPN Server.
- VPN Server will automatically restart each time the certificate file shown at Control Panel > Security > Certificate is modified.
L2TP/IPSec
L2TP (Layer 2 Tunneling Protocol) over IPSec provides virtual private networks with increased security and is supported by most clients (such as Windows, Mac, Linux, and mobile devices). For more information about L2TP, refer to here.
Note:
- To use L2TP/IPSec, make sure your Synology NAS is running DSM 4.3 or later.
To enable L2TP/IPSec VPN server:
- Open VPN Server and then go to Settings > L2TP/IPSec on the left panel.
- Tick Enable L2TP/IPSec VPN server.
- Specify a virtual IP address of VPN server in the Dynamic IP address fields. Refer to About Dynamic IP Address below for more information.
- Set Maximum connection number to limit the number of concurrent VPN connections.
- Set Maximum number of connections with same account to limit the number of concurrent VPN connections with the same account.
- Choose either of the following from the Authentication drop-down menu to authenticate VPN clients:
- PAP: VPN clients' passwords will not be encrypted during authentication.
- MS-CHAP v2: VPN clients' passwords will be encrypted during authentication using Microsoft CHAP version 2.
- Set MTU (Maximum Transmission Unit) to limit data packet size transmitted via the VPN.
- Tick Use manual DNS and specify the IP address of a DNS server to push DNS to L2TP/IPSec clients. If this option is disabled, the DNS server used by the Synology NAS will be pushed to clients.
- Enter and confirm a pre-shared key. This secret key should be given to your L2TP/IPSec VPN user to authenticate the connection.
- Click Apply for the changes to take effect.
Note:
- When connecting to the VPN, the authentication and encryption settings of VPN clients must be identical to the settings specified on VPN Server, or else clients will not be able to connect successfully.
- To be compatible with most L2TP/IPSec clients running Windows, Mac OS, iOS, and Android operating systems, the default MTU is set to 1400. For more complicated network environments, a smaller MTU might be required. Try to reduce the MTU size if you keep receiving timeout error or experience unstable connection.
- Please check the port forwarding and firewall settings on your Synology NAS and router to make sure the UDP port 1701, 500, and 4500 are open.
- L2TP or IPSec VPN service is built-in on some routers, the port 1701, 500 or 4500 might be occupied. To ensure VPN Server works properly, you might need to disable the built-in L2TP or IPSec VPN service through the router's management interface to have the L2TP/IPSec of VPN Server work. It is recommended using a router that supports VPN pass-through connections.
About Dynamic IP Address
Depending on the number you entered in Dynamic IP address, VPN Server will choose from a range of virtual IP addresses while assigning IP addresses to VPN clients. For example, if the dynamic IP address of VPN server is set as '10.0.0.0', a VPN client's virtual IP address could range from '10.0.0.1' to '10.0.0.[maximum connection number]' for PPTP, and from '10.0.0.2' to '10.0.0.255' for OpenVPN.
Important:Before specifying the dynamic IP address of VPN server, please note:
- Dynamic IP addresses allowed for VPN server should be any of the following:
- From '10.0.0.0' to '10.255.255.0'
- From '172.16.0.0' to '172.31.255.0'
- From '192.168.0.0' to '192.168.255.0'
- The specified dynamic IP address of VPN server and the assigned virtual IP addresses for VPN clients should not conflict with any IP addresses currently used within your local area network.
About Client's Gateway Setting for VPN Connection
Before connecting to the local area network of Synology NAS via VPN, the clients might need to change their gateway setting for VPN connection. Otherwise, they might not be able to connect to the Internet when VPN connection is established. For detailed information, refer to here.
A few years ago, a close friend of mine was hit with a subpoena claiming that his unsecured WiFi network was used to illegally pirate movies. Though they may have never been able to prove who exactly was pirating the movies, the legal fees would have cost thousands just to prove their innocence.
Ever since then, I've been an advocate for using VPNs to protect your privacy when browsing the web.
When I upgraded my storage solution to a NAS, one of the first settings I changed was to route my NAS internet through a VPN.
Unfortunately, this meant all my local browsing was also going through the VPN making everything slow to a crawl.
After many hours of studying different forums, Reddit, and YouTube later, I think I have found the best solution to keep your only your torrent traffic running through a VPN while all other network activities are kept local.
If you enjoy this guide and would like to support additional content creation, consider making a qualifying purchase using any of the affiliate links below.
Private Internet Access Synology Vpn
What you'll need
Here is the setup I used to get this project up and running.
I've been using Private Internet Access for many years and they work perfectly with this guide. You can check the latest pricing information here.
If you decide to use a different VPN, this guide should still get you at least 95% of the way there. Check out their respective communities on Reddit or reach out to your VPN's customer support for any additional steps.
- NAS: Synology DS918+
- DSM Version: 6.2.2 and newer
- VPN: Private Internet Access
Installation Steps
Install Docker
1. Find and install Docker in the Package Center.
2. Search the registry for haugene
3. Download the latest image for haugene/transmission-openvpn
While the image is downloading, we'll complete the next steps.
Create Transmission Directory
Next, we'll create a couple of folders. One for your Transmission configuration files and another for your downloads.
- Inside the docker folder, create a folder named transmission-openvpn
- In your root directory, create a folder named Downloads
Create Adapter and Configuration File
To create your own files, copy the scripts below into a plain text editor save the files as the following:
Optional: Since these are Google's Public domain nameservers (DNS), this may result in your container leaking website requests. To fix this, change the nameservers to your VPN's public DNS servers.
For PIA users your resolv.confshould look like this:
Free wifi booster virgin. Move these files over to your transmission-openvpn folder.
Schedule Adapter to Run on Boot
1. Open Control Panel
2. Open Task Scheduler
3. Create a Task to run the TUN.sh script on boot-up.
4. In the Task Settings, point to the location of the script.
5. Run the script for the first time.
Launch the Docker Image
Back in Docker, the image should be done downloading now. Launch the image with the following settings:
1. Execute container using high privilege
2. Select Advanced Settings
3. Enable auto-restart
4. Add the resolv.conf file and the Downloads folder.
5. Point the File/Folder to the following mount paths.
5.5 Change the Local Ports from Auto to some unused port numbers.
If you leave this on auto, you will have to constantly look up what port your container has changed to.
6. Add your VPN details into the OpenVPN Environment variables:
| OPENVPN_USERNAME | p00***** |
| OPENVPN_PASSWORD | **password** |
| OPENVPN_PROVIDER | PIA |
You can experiment with the remaining default variables after you have the container up and running.
PIA NextGen Updates
PIA has updated their VPN network to NextGen which has broken previous containers.
If you're having trouble launching your old containers, delete all of your old images and containers.
Redownload the latest image and add the additional environmental variables:
Pia Vpn On Synology Download
| OPENVPN_CONFIG | ca_montreal |
| PIA_OPENVPN_CONFIG_BUNDLE | openvpn |
All OPENVPN_CONFIG values are now lowercase and have underscores instead of spaces.
Additionally, this value can accept a list of servers to randomly connect to. e.g. ca_montreal,ca_toronto,ca_vancouver
Run Container
1. Apply the settings and launch the container.
2. Click on the container details to the local port number.
3. Open a browser, go to your local IP and container's port number. ie. 192.168.1.100:30000 or 10.0.0.1:30000.
Private vpn access. 4. You should now be connected to your transmission docker container:
Verify VPN is Working
1. To verify Transmission is working as intended, visit http://checkmyip.torrentprivacy.com/ and download the test torrent file.
2. If everything worked properly, your browsing IP should be different than your Torrent IP.
For Seeding/Uploading:
To upload/seed files, you need to select a VPN gateway that has Port Forwarding enabled.
If you are using PIA, you can find more information here: https://www.privateinternetaccess.com/helpdesk/kb/articles/how-do-i-enable-port-forwarding-on-my-vpn
Currently the enabled gateways values that support port forwarding are:
- ca_montreal
- ca_toronto
- ca_vancouver
- czech_republic
- france
- de_berlin
- de_frankfurt
- israel
- romania
- spain
- sweden
- switzerland
1. To force the container to use a specific server, add the following Environment Variable to point it to an enabled gateway.
- OPENVPN_CONFIG: ca_montreal
2. To verify this is working, open the Transmission Settings and go to the Network Tab. The Peer Listening port should say Open.
Congrats!
You now have a Docker container of Transmission connected through a VPN provider.
Simply add torrents to Transmission and your downloads will appear in your Downloads folder when they are completed.
Other Tidbits
The Chrome Extensions Remote Transmission ++ is a great tool that allows you to open up magnet links without having to open up the full-blown Transmission web interface. Thanks to bricked3ds for sharing this on Reddit.

